Today we'll learn about carbohydrates, a essential polymer that needs by our body as well as the other organisms too. Ok, let's start! (ecehh,,poyo kot..haha)

First thing first, let's do a little briefing about carbohydrates. Carbohydrates is consists of element C,H and O, which include:
MONOSACCHARIDES





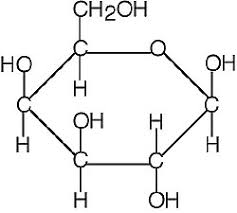
galactose
- Monosaccharides
- Disaccharides/oligosaccharides
- Polysaccharides
just proceed to the components of carbohydrates...
MONOSACCHARIDES
- the simple sugars of (CHnO)n, where n=3,4,5,6,7. (more than 7 is not a monosaccharide)
- the simplest form of sugar, cannot be hydrolysed anymore.
- Divided into two types, aldose and ketose.
- Each monosaccharide MUST have one hydroxyl (-OH) and one carbonyl (=O) group
- Structure of monosaccharide can be represented in THREE ways,
- straight chain (Fischer Projection)
- cyclic/ring form (Haworth Projection)
- chair/boat form.
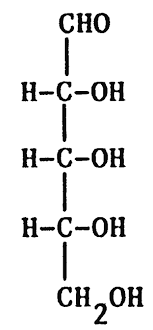
Fischer projection
Haworth Projection

Chair Form

IN HAWORTH FORM
*Glucose can form over 16 isomers. Yet, the most important types (that you must remember) are:
- D and L isomerism
- Epimers
- Aldose-ketose isomerism
- Pyranose and furanose ring strutures
- Alpha and beta anomers
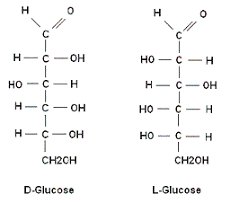
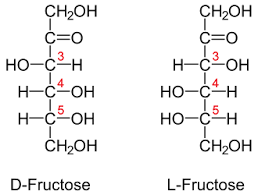
D and L isomerism
The position of H and OH in carbon number 5 (C5) determines whether the sugar belongs to D or the L series.
If -OH on the right, the sugar is the D isomer
If -OH on the left, the sugar is the L isomer. *Note: L=LEFT
Epimers
Isomers that differs due to the variation of H and OH position on C2, C3 and C4 of the glucose:
At C2 and C4, if -OH on the right, the sugar is glucose
At C2, If -OH on the left, the sugar is mannose
At C4, if -OH on the left, the sugar is galactose
*the carbon where the rotation occurs is called the anomeric carbon
Aldose-Ketose Isomerism
Depends on the position of the carbonyl group. If, the carbonyl in C1, the sugar is aldose. If the carbonyl group is in C2, it is a ketose. In this chapter, we use glucose as aldehyde while fructose as ketones.
Pyranose and Furanose Ring
Those with 5 membered ring structure (furan) are called furanoses, while one with 6 membered rings (pyran) are called pyranose.
(in Haworth projection -ring form)
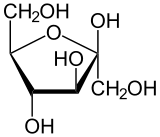


p/s: how the ring can be formed. The H on the fifth carbon (C5) combine with O at the first carbon. The remaining O (kan asalnya OH) become the connector.
FURANOSE (5) PYRANOSE (6)
p/s: how the ring can be formed. The H on the fifth carbon (C5) combine with O at the first carbon. The remaining O (kan asalnya OH) become the connector.
Ok, masuk pulak pada jenis2 monosaccharide mengikut bilangan CARBON ATOM
Yang kitorang belajar ade triose(3), pentose (5), hexose (6).
PENTOSE
- Molcular formula : C5H10O5
- Example: Ribose and Deoxyribose
- D-Ribose found in coenzymes, ATP and RNA
IN FISCHER PROJECTION
IN HAWORTH FORM
*beza deoxyribose dengan ribose ialah komponen pada C ke 2 dalam ring form. Ribose: OH, Deoxyribose:H
Hexose
Molcular formula : C6H10O6
Example (the most common): glucose, galactose, fructose------>strukur2 dy dah dibezakan masa kat atas tadi
*All the three hexoses share the same molecular formula but ARRANGEMENT OF THE ATOMS are DIFFERENT (structural isomers)
Example (the most common): glucose, galactose, fructose------>strukur2 dy dah dibezakan masa kat atas tadi
*All the three hexoses share the same molecular formula but ARRANGEMENT OF THE ATOMS are DIFFERENT (structural isomers)
galactose
bersambung kemudian...bnyaaaaak lagi ni.>!! yada2~
Ingatlah hadith nabi: Rasulullah s.a.w bersabda, maksudnya:
"Siapa yang keluar untuk menuntut ilmu maka ia berjuang fisabilillah hingga ia kembali".
Sekian :)
